Page 58 - Taiwan Food and Drug Administration 2016 Annual Report
P. 58
Taiwan Food and Drug Adminstration
( Number )
4,000
3,500 3,453
3,000
2,500
2,000
1,634
1,500 1,368 1,401
1,000 748
500 144 209 375
30 157 54 366 70 85
0
98 99 100 101 102 103 104 ( Year )
Number of ADR reports Number of defective products
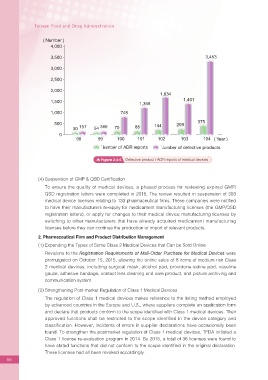
Figure 2-4-6 Defective product / ADR reports of medical devices
(4) Suspension of GMP & QSD Certi?cation
To ensure the quality of medical devices, a phased process for reviewing expired GMP/
QSD registration letters were completed in 2015. The review resulted in suspension of 303
medical device licenses relating to 133 pharmaceutical ?rms. These companies were noti?ed
to have their manufacturers re-apply for medicament manufacturing licenses (the GMP/QSD
registration letters), or apply for changes to their medical device manufacturing licenses by
switching to other manufacturers that have already acquired medicament manufacturing
licenses before they can continue the production or import of relevant products.
2. Pharmaceutical Firm and Product Distribution Management
(1) Expanding the Types of Some Class 2 Medical Devices that Can be Sold Online
Revisions to the Registration Requirements of Mail-Order Purchase for Medical Devices were
promulgated on October 15, 2015, allowing the online sales of 8 items of medium risk Class
2 medical devices, including surgical mask, alcohol pad, providone-iodine pad, vaseline
gauze, adhesive bandage, contact lens cleaning and care product, and picture archiving and
communication system.
(2) Strengthening Post-market Regulation of Class 1 Medical Devices
The regulation of Class 1 medical devices makes reference to the listing method employed
by advanced countries in the Europe and U.S., where suppliers complete an application form
and declare that products conform to the scope identi?ed with Class 1 medical devices. Their
approved functions shall be restricted to the scope identified in the device category and
classification. However, incidents of errors in supplier declarations have occasionally been
found. To strengthen the postmarket regulation of Class 1 medical devices, TFDA initiated a
Class 1 license re-evaluation program in 2014. By 2015, a total of 36 licenses were found to
have stated functions that did not conform to the scope identi?ed in the original declaration.
These licenses had all been revoked accordingly.
56