Page 12 - 2017食品藥物管理署年報(英文版)
P. 12
2017 Taiwan Food and Drug Administration Annual Report
surveillance of food products, in order to ensure food sanitation, safety and quality. TFDA
also uses multiple channels to communicate with consumers in order to promote and
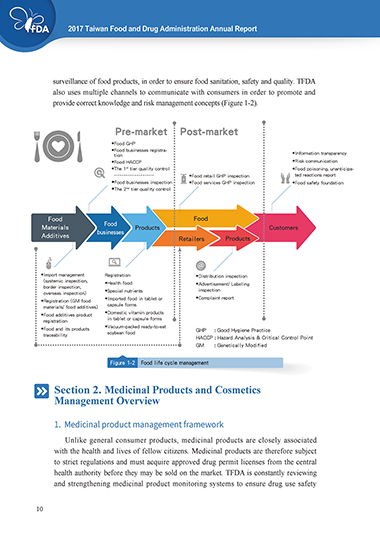
provide correct knowledge and risk management concepts (Figure 1-2).
Pre-market Post-market
◆ Food GHP
◆ Food businesses registra-
tion ◆ Information transparency
◆ Food HACCP ◆ Risk communication
◆ The 1 tier quality control ◆ Food poisoning, unanticipa-
st
⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯⋯ ◆ Food retail GHP inspection ted reactions report
◆ Food businesses inspection ◆ Food services GHP inspection ◆ Food safety foundation
◆ The 2 tier quality control
nd
Food Food
Materials Food Products Customers
Additives businesses
Retailers Products
◆ Import management Registration ◆ Distribution inspection
(systemic inspection, ◆ Health food ◆ Advertisement/ Labeling
border inspection, ◆ Special nutrients inspection
overseas inspection)
◆ Imported food in tablet or ◆ Complaint report
◆ Registration (GM food
materials/ food additives) capsule forms
◆ Domestic vitamin products
◆ Food additives product
registration in tablet or capsule forms
◆ Vacuum-packed ready-to-eat
◆ Food and its products GHP : Good Hygiene Practice
traceability soybean food HACCP : Hazard Analysis & Critical Control Point
GM : Genetically Modified
Figure 1-2 Food life cycle management
Section 2. Medicinal Products and Cosmetics
Management Overview
1. Medicinal product management framework
Unlike general consumer products, medicinal products are closely associated
with the health and lives of fellow citizens. Medicinal products are therefore subject
to strict regulations and must acquire approved drug permit licenses from the central
health authority before they may be sold on the market. TFDA is constantly reviewing
and strengthening medicinal product monitoring systems to ensure drug use safety
10